Choosing the right pipe for water supply is a crucial task for homeowners, contractors, and builders alike. Whether you’re embarking on a new construction project or upgrading an existing plumbing system, the type of pipe you select can significantly influence the safety, longevity, and efficiency of your setup. A dependable water supply pipe not only ensures access to clean drinking water but also minimizes leaks and helps keep long-term maintenance costs down.
With a myriad of options available today, deciding on the best fit for your needs can be daunting. You’ll want to consider factors like water temperature, quality, budget, and the pipe’s durability. In this guide, we’ll provide a comprehensive look at the types of water supply pipes, weighing their pros and cons, and offering expert insights to assist you in selecting the most suitable pipe for your home or business.
Understanding Water Supply Pipes
The primary role of a water supply pipe is to transport clean water from the main source to various outlets such as faucets, bathrooms, kitchens, and other fixtures. Whether you’re constructing a single-family home or designing an expansive commercial facility, picking the right pipe material is essential for ensuring long-term performance and safety.
For plumbing projects, especially those focused on residential systems, the pipe material needs to be not only durable but also hygienic and resistant to common issues like corrosion and leaks. Water supply pipes are generally categorized by their material, ranging from traditional metal options like copper and galvanized iron (GI) to contemporary choices such as PVC, CPVC, and UPVC.
Each pipe type has its unique advantages and disadvantages, which we will examine in detail.
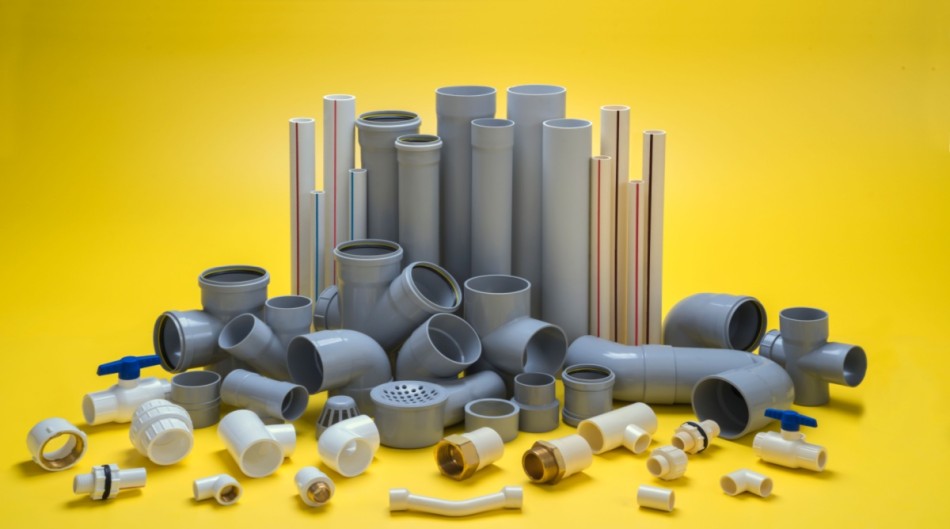
Types of Water Supply Pipes
Different projects require specific types of water supply pipes based on factors like durability, application, and cost. Here’s a brief overview of some of the most widely used pipe types:
-
PVC Pipes (Polyvinyl Chloride)
– Lightweight, budget-friendly, and easy to install.
– Pros: Best for cold water supply, corrosion-resistant, and affordable.
– Cons: Not suitable for hot water due to low heat tolerance.
– Best for: Outdoor irrigation, cold water pipelines, and residential plumbing.
-
CPVC Pipes (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride)
– An upgraded variant of PVC that can handle higher temperatures.
– Pros: Versatile for both hot and cold water supply, chemical-resistant, and durable.
– Cons: Slightly pricier than PVC pipes.
– Best for: Indoor plumbing, hot water pipelines, and modern homes.
-
UPVC Pipes (Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride)
UPVC pipes stand out for their impressive durability and the absence of plasticizing agents, making them an environmentally friendly choice.
– Pros: They are corrosion-free, resistant to chemicals, and designed for longevity.
– Cons: Their use for hot water applications is somewhat limited.
– Best for: Ideal for cold water supply in both residential and commercial buildings.
-
PEX Pipes (Cross-linked Polyethylene)
PEX pipes are known for their flexibility and versatility, making them a popular selection for modern plumbing setups.
– Pros: They can easily bend into tight spaces, resist both hot and cold temperatures, and are quick to install.
– Cons: They are sensitive to UV light and may need protective insulation for outdoor usage.
– Best for: Great for concealed piping systems, radiant heating, and both hot and cold water lines.
-
Copper Pipes
Copper pipes have long been regarded as a traditional and reliable option in plumbing.
– Pros: They resist corrosion and high temperatures, offer long-lasting performance, and are recyclable.
– Cons: Their cost can be high, and professional installation is typically necessary.
– Best for: Particularly suited for specialized applications, such as hospitals or areas where high water quality standards are crucial.
-
Galvanized Iron (GI) Pipes
While once a popular choice, GI pipes are now gradually being replaced due to their tendency to rust.
– Pros: They are strong, durable, and capable of handling high pressure.
– Cons: They can be prone to rust and contamination over time, are heavy, and can be complicated to install.
– Best for: Most suitable for industrial settings and high-pressure water systems.